Thyroid Cancer
Understanding Thyroid Cancer
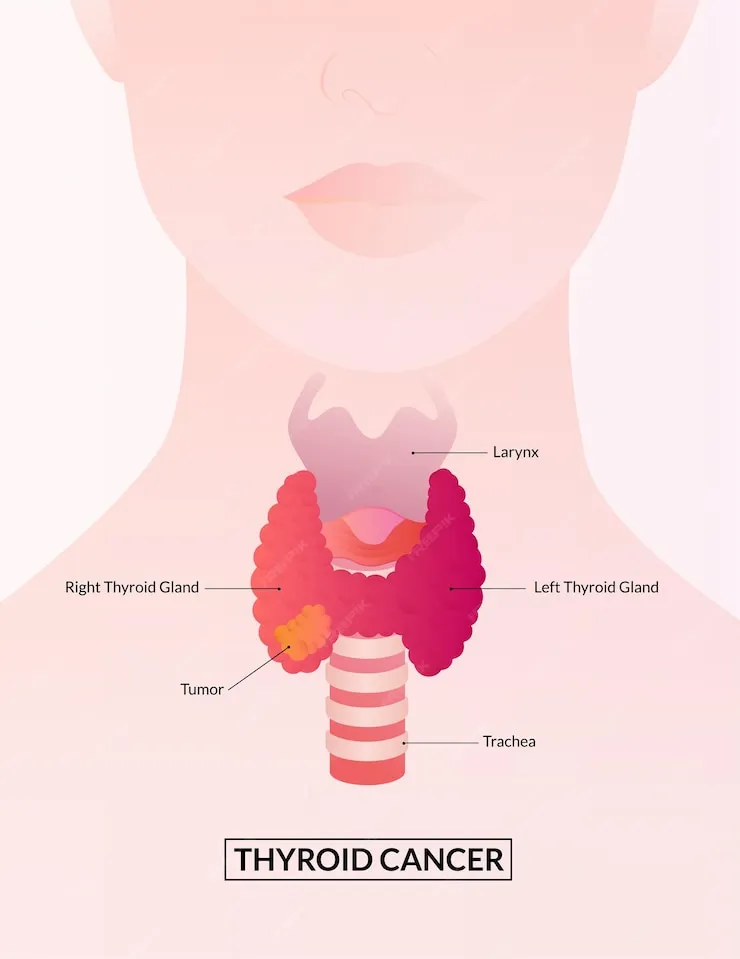
Thyroid cancer is a type of malignancy that originates in the cells of the thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. It's a relatively rare form of cancer but can occur at any age. Understanding this condition involves recognizing its types, causes, and treatment options.
Types of Thyroid Cancer
Papillary Thyroid Cancer: This is the most common type, accounting for about 80% of thyroid cancer cases. It tends to grow slowly and usually remains confined to the thyroid gland initially.
Follicular Thyroid Cancer: This type accounts for approximately 10-15% of thyroid cancer cases. It often spreads to nearby lymph nodes and can invade blood vessels.
Medullary Thyroid Cancer: This type is less common, arising in the C cells of the thyroid that produce calcitonin. It may also run in families and can spread to lymph nodes and distant organs.
Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: This is the most aggressive and least common form of thyroid cancer. It rapidly grows and spreads to nearby structures in the neck.
Causes and Risk Factors
Thyroid cancer often occurs due to genetic mutations in thyroid cells. While the exact cause isn't always clear, some risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing this cancer, including radiation exposure, certain inherited genetic syndromes, and a family history of thyroid cancer.
Treatment Options
Treatment for thyroid cancer depends on the type, stage, and individual patient factors. Common approaches include:
- Surgery: The primary treatment involves surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy). Lymph nodes in the neck might also be removed.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: This treatment, often used after surgery, involves taking radioactive iodine orally. The iodine is absorbed by any remaining thyroid tissue to destroy cancerous cells.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: After surgery, patients might need to take synthetic thyroid hormone to replace the hormones no longer produced by the thyroid.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy: In cases where cancer spreads or returns after initial treatments, external radiation therapy may be utilized.
- Targeted Drug Therapy: For advanced or recurrent thyroid cancer, targeted drug therapies may be employed to inhibit specific cancerous processes.
Treatment plans are personalized based on the cancer's stage, the patient's overall health, and other factors, often involving a multidisciplinary approach with endocrinologists, surgeons, oncologists, and other specialists. Regular follow-ups are crucial to monitor progress and manage any potential recurrence.
Dr. Aun Jamal?
Testimonials from Our Patients
Posted on
Request
Appointment Today
Call Us
03074443322
24/7 Support
Book Now
Location
Evercare Hospital Lahore
